Susan Walsh / pool via Reuters file
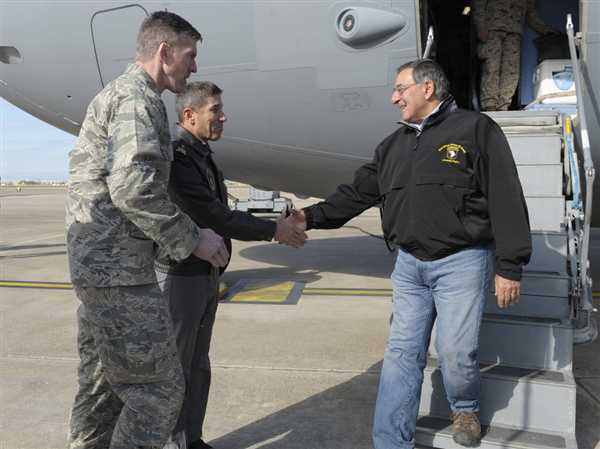
U.S. Defense Secretary Leon Panetta is greeted by Brig. Gen Serdar Gulbas, center, and Col. Christopher E. Craige during a stopover to visit U.S. troops in Turkey on Dec. 14.
The Center for Public Integrity
The Obama administration has quietly arranged for thousands of chemical protective suits and related items to be sent to Jordan and Turkey and is pressing the military forces there to take principal responsibility for safeguarding Syrian chemical weapons sites if the country’s lethal nerve agents suddenly become vulnerable to theft and misuse, Western and Middle Eastern officials say.
As part of their preparations for such an event, Western governments have started training the Jordanians and Turks to use the chemical gear and detection equipment, so they have the capability to protect the Syrian nerve agent depots if needed – at least for a short time, U.S. and Western officials say.
Washington has decided moreover that the best course of action in the aftermath of Syrian President Bashar Assad’s fall would be to get the nerve agents out of the country as quickly as possible, and so it has begun discussions not only with Jordan and Turkey, but also with Iraq and Russia in an effort to chart the potential withdrawal of the arsenal and its destruction elsewhere.
Using allied forces from Syria’s periphery as the most likely “first-responders” to a weapons-of-mass-destruction emergency is regarded in Washington as a way to avoid putting substantial U.S. troops into the region if the special Syrian military forces now safeguarding the weapons leave their posts. A Syrian withdrawal might otherwise render the weapons vulnerable to capture and use by Hezbollah or other anti-U.S. or anti-Israeli militant groups, U.S. officials fear.
This article is based on conversations about international planning for the disposition of the Syrian stockpile with a half dozen U.S. and foreign officials who have direct knowledge of the matter but declined to be named due to the political and security sensitivities surrounding their work.
They said the Western planning, while not yet complete, is further along than officials have publicly disclosed.
But so far, the Turkish and Jordanian governments have not promised to take up the full role that Washington has sought to give them, U.S. and foreign officials said.
Asked for comment, Jordanian embassy spokeswoman, Dana Zureikat Daoud, said the training under way is “not mission-oriented,” meaning that Jordan does not have a fixed responsibility. But she added that the government is indeed concerned about the possibility of Syrian chemical armaments falling into extremist hands. “Our contingency plans … are discussed and elaborated with like-minded, concerned countries,” she said.
A spokesman at the Turkish Embassy declined comment. But James F. Jeffrey, the U.S. ambassador to Turkey from 2008-2010, said that although Ankara is eager for the United States to play a larger role in resolving the Syrian crisis, the Turks are “usually reluctant to be our foot-soldiers.” He added: “When Americans come up with a plan to use country x’s soldiers, the plan is often self-fulfilling inside the Beltway,” but sometimes runs into trouble when it is broached in foreign capitals.
The prospect of lethal nerve agents at any Syrian sites suddenly becoming unprotected is one of many alarming developments that have been war-gamed at the Pentagon over the past year, as the conflict there deepens and president Assad’s grip over his deadly arsenal comes into greater question, U.S. officials say.
Private messages to Syrian commanders
Worries about the fate of the chemicals – in a stockpile estimated at 350 to 400 metric tons — have become so great that Washington and its allies have recently passed messages to some of the Syrian commanders that oversee their security, offering safety and a continued role under a new government if the commanders act responsibly, two knowledgeable officials said on condition they not be named.
It is unclear what the results of that effort have been. But similar messages, urging restraint and good behavior in handling the chemicals, have also been passed in recent weeks to rebel forces inside the country, according to a Western official.
One of Washington’s concerns has been that Assad might order the chemicals used against his own citizens, a fear that spiked late last year when chemicals at one base were seen being loaded into artillery shells and bombs. Western and Russian officials issued stiff warnings, and those concerns abated somewhat, although Foreign Policy magazine reported Jan. 15 that some evidence exists that Syria used a generally nonlethal incapacitating gas against rebels in Homs last month.
“We found no credible evidence to corroborate or to confirm that chemical weapons were used” in that incident, State Department spokeswoman Victoria Nuland said on Tuesday.
The principal U.S. concern in a post-Assad period, Secretary of Defense Leon Panetta said at a press briefing on Jan. 10, is “how do we secure the CBW (chemical and biological weapons) sites?…And that is a discussion that we are having, not only with the Israelis, but with other countries in the region, to try to look at … what steps need to be taken in order to make sure that these sites are secured.”
“We’re not working on options that involve (U.S.) boots on the ground,” Panetta said.
At one extreme, officials said, special forces now in the region might have to intervene on short notice if it appears that weapons at one of the sites are about to fall into the wrong hands or to be employed on a large scale. They would be tasked with swiftly neutralizing both the agent and any hostile forces present and likely stay on the ground only for a few hours.
The Obama administration’s preference is to have other nations’ forces undertake such an intervention, and so the United States and Britain have been conducting joint planning and training operations with Jordanian and Turkish commandos for more than a year, to prepare for their possible emergency insertion into Syria, according to U.S. and foreign officials familiar with the plans.
The protective suits, along with detection equipment and decontamination gear, began arriving in the late fall amid concern that the Syrian government might be considering using the weapons to halt rebel advances. Syria’s arsenal – which was developed for a potential conflict with Israel — includes mustard gas, which burns and blisters the skin and lungs, More problematically, it also includes sarin and VX, liquids that interfere with the nervous system and produce swift death by paralysis after minute, drop-size exposures, U.S. officials say.
Syria devised its nerve weapons as binary agents, in which two less toxic chemicals are routinely stored in large, separated canisters and then loaded into separate compartments inside a bomb. For example, sarin uses a formulation of alcohol, plus another chemical. The agents combine to pose their most lethal threat only when launched or during flight, making them relatively easy to handle or transport before then – by the Syrian military or by terrorists and militant groups.
Syria regime ‘reeling, armed to the teeth’ with chemical weapons
But the separation of the basic components also opens the door to at least a partial elimination of the threat onsite, since the alcohol used in sarin could simply be drained onto the ground and allowed to evaporate.
Jordan and Turkey initially agreed to undertake Western training in dealing with chemical weapons because they might have to deal with panicked refugees and victims if Assad’s forces use such arms against the rebels; some risk also exists in that circumstance of clouds of dangerous gas wafting onto their own territory from Syrian cities near their border. Even medical workers would be at grave risk in dealing with those who became contaminated; as a result, they are being trained now by Western powers, according to foreign officials.
“Their primary concern is a spillover of these things into their territory,” one U.S. official said. The salience of this worry was demonstrated when a Syrian mortar round crashed into a Turkish field near a refugee camp on Jan. 14. As Daoud, the Jordanian spokeswoman, said, “Naturally, we will do everything that needs to be done to defend our people and our borders.”
Seeking Assad exit strategy
Partly because of worries about the stockpile’s security, Washington and its allies still hope that Assad might be persuaded to leave in exchange for a guarantee of his personal security elsewhere. In such a negotiated transition, Western powers would seek to keep the existing Syrian military units responsible for safeguarding the chemical weapons sites in place, officials said.
“The people in Assad’s regime responsible for security at the chemical sites are among the very best soldiers,” a U.S. official said. “If one could keep those forces in place … that would be the best and probably the cheapest and most efficient outcome.”
But Assad, in a defiant address on Jan. 6, said he had no intention of stepping aside or negotiating with the rebels engaged in a bitter struggle for national control that so far has claimed at least 60,000 lives.
“We’re engaged in planning to develop options against alternative futures … (including) collaboration or cooperation, permissiveness, non-permissive, hostile, all of which would have different requirements,” Joint Chiefs of Staff chairman Gen. Martin Dempsey said at the Jan. 10 briefing.
“The options are not good in any scenario,” said another senior official, adding that Washington is as worried about the chemicals falling into the hands of rebel forces that may seize power, either locally or nationally, as it is about their misuse by terrorists or by rogue Syrian military units and commanders. At least one of the major Syrian rebel groups, Jabhat al-Nasra, has been designated by the United States as a terrorist organization.
Also, U.S. intelligence agencies have warned policymakers that once Assad is gone, the country’s turmoil will increase, with rival groups potentially seeking to brandish possession of the chemical weapons as symbols of their power. Officials said that as a result, they have pressed the Syrian National Coalition, a rebel group recognized by Western countries, to appoint a coordinator now for all chemical weapons-related policymaking and negotiations.
Simply blowing up the chemicals inside Syria with bombs or other weapons is not an option, as Panetta made clear in a briefing for reporters during a December visit to Turkey: He said the plumes from such explosions would cause “exactly the kind of damage” that would result from the weapons’ deliberate use.
Incinerating the chemicals inside Syria would be logistically challenging and pose high security risks, since Western countries have only a few portable destruction kits for chemical weapons, developed primarily to deal with single, leaking shells, not large stocks.
As a result, U.S. officials said they would likely seek to transport the chemicals out of Syria as quickly as possible once a new government can be formed, preferably under the supervision of the United Nations-affiliated Organization for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons, with the new government’s formal approval.
“We maintain regular communication with States Parties as well as the United Nations on developments in Syria and continue our efforts to prepare for various scenarios which could potentially involve the OPCW in that situation,” said OPCW spokesman Michael Luhan.
Under one scenario now under discussion between Washington and its allies, the chemicals would be moved to secure military bases in Jordan, Turkey or Iraq, where the United States and others would erect chemical incinerators over a six- to 12-month period that could destroy the bulk agent in a year or so after that. Using similar incinerators to destroy a small stockpile of chemical weapons in Albania more than five years ago cost $48 million.
But even this task would be logistically awkward, not to mention politically controversial in those states. Undertaking it would first require further consolidation of the stocks inside Syria and then their transport outside the country in hundreds of truckloads.
Russia said to offer help
Another option, which officials said has tentatively been explored with senior Russian officials, is to truck the chemical agents to the Syrian port of Tartus, where the Russian Navy keeps a small presence, so that the arsenal could be placed on a ship for transport to Russia, where multiple chemical weapons destruction plants have been constructed with Western help.
By the accounts of several officials, Russia has expressed some desire to help. And Western officials emphasized that in their view, the country has a special responsibility to do so, because of reports that the head of its chemical weapons program helped Syria obtain key VX components in the early 1990s.
No final policy choice has been made about these options, senior officials said. And bringing a large weapons stockpile into Turkey or Russia – which are signatories of an international treaty barring use or possession of chemical arms – might require a waiver of the treaty’s rules against importing even the components of such weapons.
Some consolidation of the Syrian arsenal has already occurred on Assad’s orders, and the bulk of it is now at fewer than a dozen sites, according to a U.S. official familiar with intelligence estimates.
But U.S. military planners are unsure precisely how many sites might hold deadly chemicals at the point that a foreign intervention would be necessary or feasible. If Assad disperses the arsenal beforehand to the 40 or so military bases with aircraft or missiles that can drop or launch the weapons, as many as 75,000 foreign troops could be needed to contain the threat (several thousand troops at each base, according to this worst-case estimate). A smaller number would be needed if the intervention preceded such a dispersal.
The shipment of protective gear to Syria’s periphery from U.S. and British stockpiles was an acknowledgement of the enormity of the problem, several officials said. They described thousands of pieces of chemical-protection gear — from masks and suits to detectors and decontamination kits — being pre-positioned in Jordan alone.
Asked for comment, Joint Chiefs of Staff spokesman Scott McIlnay responded that “we have always said that contingency planning is the responsible thing to do, and we are actively consulting with friends, allies and the opposition. But I am not going to get into the specifics of our contingency plans.” Pentagon spokesman Bryan Whitman said he could only say that “we are working with our partners in the region and the broader international community to monitor the situation and discussing contingencies.”
The Center for Public Integrity is a nonprofit independent investigative news outlet. To read more of its stories on this topic go to publicintegrity.org