F. William Engdahl, February 5, 2011
Fast on the heels of the regime change in Tunisia came a popular-based protest movement launched on January 25 against the entrenched order of Egypt’s Hosni Mubarak. Contrary to the carefully-cultivated impression that the Obama Administration is trying to retain the present regime of Mubarak, Washington in fact is orchestrating the Egyptian as well as other regional regime changes from Syria to Yemen to Jordan and well beyond in a process some refer to as “creative destruction.”
The template for such covert regime change has been developed by the Pentagon, US intelligence agencies and various think-tanks such as RAND Corporation over decades, beginning with the May 1968 destabilization of the de Gaulle presidency in France. This is the first time since the US backed regime changes in Eastern Europe some two decades back that Washington has initiated simultaneous operations in many countries in a region. It is a strategy born of a certain desperation and one not without significant risk for the Pentagon and for the long-term Wall Street agenda. What the outcome will be for the peoples of the region and for the world is as yet unclear.
Yet while the ultimate outcome of defiant street protests in Cairo and across Egypt and the Islamic world remains unclear, the broad outlines of a US covert strategy are already clear.
No one can dispute the genuine grievances motivating millions to take to the streets at risk of life. No one can defend atrocities of the Mubarak regime and its torture and repression of dissent. Noone can dispute the explosive rise in food prices as Chicago and Wall Street commodity speculators, and the conversion of American farmland to the insane cultivation of corn for ethanol fuel drive grain prices through the roof. Egypt is the world’s largest wheat importer, much of it from the USA. Chicago wheat futures rose by a staggering 74% between June and November 2010 leading to an Egyptian food price inflation of some 30% despite government subsidies.
What is widely ignored in the CNN and BBC and other Western media coverage of the Egypt events is the fact that whatever his excesses at home, Egypt’s Mubarak represented a major obstacle within the region to the larger US agenda.
To say relations between Obama and Mubarak were ice cold from the outset would be no exaggeration. Mubarak was staunchly opposed to Obama policies on Iran and how to deal with its nuclear program, on Obama policies towards the Persian Gulf states, to Syria and to Lebanon as well as to the Palestinians.1 He was a formidable thorn in the larger Washington agenda for the entire region, Washington’s Greater Middle East Project, more recently redubbed the milder sounding “New Middle East.”
As real as the factors are that are driving millions into the streets across North Africa and the Middle East, what cannot be ignored is the fact that Washington is deciding the timing and as they see it, trying to shape the ultimate outcome of comprehensive regime change destabilizations across the Islamic world. The day of the remarkably well-coordinated popular demonstrations demanding Mubarak step down, key members of the Egyptian military command including Chief of General Staff Lt. Gen. Sami Hafez Enan were all in Washington as guests of the Pentagon. That conveniently neutralized the decisive force of the Army to stop the anti-Mubarak protests from growing in the critical early days.2
The strategy had been in various State Department and Pentagon files since at least a decade or longer. After George W. Bush declared a War on Terror in 2001 it was called the Greater Middle East Project. Today it is known as the less threatening-sounding “New Middle East” project. It is a strategy to break open the states of the region from Morocco to Afghanistan, the region defined by David Rockefeller’s friend Samuel Huntington in his infamous Clash of Civilizations essay in Foreign Affairs.
Egypt rising?
The current Pentagon scenario for Egypt reads like a Cecil B. DeMille Hollywood spectacular, only this one with a cast of millions of Twitter-savvy well-trained youth, networks of Muslim Brotherhood operatives, working with a US-trained military. In the starring role of the new production at the moment is none other than a Nobel Peace Prize winner who conveniently appears to pull all the threads of opposition to the ancien regime into what appears as a seamless transition into a New Egypt under a self-proclaimed liberal democratic revolution.
Some background on the actors on the ground is useful before looking at what Washington’s long term strategic plan might be for the Islamic world from North Africa to the Persian Gulf and ultimately into the Islamic populations of Central Asia, to the borders of China and Russia.
Washington ‘soft’ revolutions
The protests that led to the abrupt firing of the entire Egyptian government by President Mubarak on the heels of the panicked flight of Tunisia’s Ben Ali into a Saudi exile are not at all as “spontaneous” as the Obama White House, Clinton State Department or CNN, BBC and other major media in the West make them to be.
They are being organized in a Ukrainian-style high-tech electronic fashion with large internet-linked networks of youth tied to Mohammed ElBaradei and the banned and murky secret Muslim Brotherhood, whose links to British and American intelligence and freemasonry are widely reported.3
At this point the anti-Mubarak movement looks like anything but a threat to US influence in the region, quite the opposite. It has all the footprints of another US-backed regime change along the model of the 2003-2004 Color Revolutions in Georgia and Ukraine and the failed Green Revolution against Iran’s Ahmedinejad in 2009.
The call for an Egyptian general strike and a January 25 Day of Anger that sparked the mass protests demanding Mubarak resign was issued by a Facebook-based organization calling itself the April 6 Movement. The protests were so substantial and well-organized that it forced Mubarak to ask his cabinet to resign and appoint a new vice president, Gen. Omar Suleiman, former Minister of Intelligence.
April 6 is headed by one Ahmed Maher Ibrahim, a 29-year-old civil engineer, who set up the Facebook site to support a workers’ call for a strike on April 6, 2008.
According to a New York Times account from 2009, some 800,000 Egyptians, most youth, were already then Facebook or Twitter members. In an interview with the Washington-based Carnegie Endowment, April 6 Movement head Maher stated, “Being the first youth movement in Egypt to use internet-based modes of communication like Facebook and Twitter, we aim to promote democracy by encouraging public involvement in the political process.”4
Maher also announced that his April 6 Movement backs former UN International Atomic Energy Aagency (IAEA) head and declared Egyptian Presidential candidate, ElBaradei along with ElBaradei’s National Association for Change (NAC) coalition. The NAC includes among others George Ishak, a leader in Kefaya Movement, and Mohamed Saad El-Katatni, president of the parliamentary bloc of the controversial Ikhwan or Muslim Brotherhood.5
Today Kefaya is at the center of the unfolding Egyptian events. Not far in the background is the more discreet Muslim Brotherhood.
ElBaradei at this point is being projected as the central figure in a future Egyptian parliamentary democratic change. Curiously, though he has not lived in Egypt for the past thirty years, he has won the backing of every imaginable part of the Eyptian political spectrum from communists to Muslim Brotherhood to Kefaya and April 6 young activists.6 Judging from the calm demeanour ElBaradei presents these days to CNN interviewers, he also likely has the backing of leading Egyptian generals opposed to the Mubarak rule for whatever reasons as well as some very influential persons in Washington.
Kefaya—Pentagon ‘non-violent warfare’
Kefaya is at the heart of mobilizing the Egyptian protest demonstrations that back ElBaradei’s candidacy. The word Kefaya translates to “enough!”
Curiously, the planners at the Washington National Endowment for Democracy (NED)7 and related color revolution NGOs apparently were bereft of creative new catchy names for their Egyptian Color Revolution. In their November 2003 Rose Revolution in Georgia, the US-financed NGOs chose the catch word, Kmara! In order to identify the youth-based regime change movement. Kmara in Georgian also means “enough!”
Like Kefaya, Kmara in Georgia was also built by the Washington-financed trainers from the NED and other groups such as Gene Sharp’s misleadingly-named Albert Einstein Institution which uses what Sharp once identified as “non-violence as a method of warfare.”8
The various youth networks in Georgia as in Kefaya were carefully trained as a loose, decentralized network of cells, deliberately avoiding a central organization that could be broken and could have brought the movement to a halt. Training of activists in techniques of non-violent resistance was done at sports facilities, making it appear innocuous. Activists were also given training in political marketing, media relations, mobilization and recruiting skills.
The formal name of Kefaya is Egyptian Movement for Change. It was founded in 2004 by select Egyptian intellectuals at the home of Abu ‘l-Ala Madi, leader of the al-Wasat party, a party reportedly created by the Muslim Brotherhood.9 Kefaya was created as a coalition movement united only by the call for an end Mubarak’s rule.
Kefaya as part of the amorphous April 6 Movement capitalized early on new social media and digital technology as its main means of mobilization. In particular, political blogging, posting uncensored youtube shorts and photographic images were skillfully and extremely professionally used. At a rally already back in December 2009 Kefaya had announced support for the candidacy of Mohammed ElBaradei for the 2011 Egyptian elections.10
RAND and Kefaya
No less a US defense establishment think-tank than the RAND Corporation has conducted a detailed study of Kefaya. The Kefaya study as RAND themselves note, was “sponsored by the Office of the Secretary of Defense, the Joint Staff, the Unified Combatant Commands, the Department of the Navy, the Marine Corps, the defense agencies, and the defense Intelligence Community.”11
A nicer bunch of democratically-oriented gentlemen and women could hardly be found.
In their 2008 report to the Pentagon, the RAND researchers noted the following in relation to Egypt’s Kefaya:
“The United States has professed an interest in greater democratization in the Arab world, particularly since the September 2001 attacks by terrorists from Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, Egypt, and Lebanon. This interest has been part of an effort to reduce destabilizing political violence and terrorism. As President George W. Bush noted in a 2003 address to the National Endowment for Democracy, “As long as the Middle East remains a place where freedom does not flourish, it will remain a place of stagnation, resentment, and violence ready for export” (The White House, 2003). The United States has used varying means to pursue democratization, including a military intervention that, though launched for other reasons, had the installation of a democratic government as one of its end goals.
However, indigenous reform movements are best positioned to advance democratization in their own country.”12
RAND researchers have spent years perfecting techniques of unconventional regime change under the name “swarming,” the method of deploying mass mobs of digitally-linked youth in hit-and-run protest formations moving like swarms of bees.13
Washington and the stable of “human rights” and “democracy” and “non-violence” NGOs it oversees, over the past decade or more has increasingly relied on sophisticated “spontaneous” nurturing of local indigenous protest movements to create pro-Washington regime change and to advance the Pentagon agenda of global Full Spectrum Dominance. As the RAND study of Kefaya states in its concluding recommendations to the Pentagon:
“The US government already supports reform efforts through organizations such as the US Agency for International Development and the United Nations Development Programme. Given the current negative popular standing of the United States in the region, US support for reform initiatives is best carried out through nongovernmental and nonprofit institutions.“14
The RAND 2008 study was even more concrete about future US Government support for Egyptian and other “reform” movements:
“The US government should encourage nongovernmental organizations to offer training to reformers, including guidance on coalition building and how to deal with internal differences in pursuit of democratic reform. Academic institutions (or even nongovernmental organizations associated with US political parties, such as the International Republican Institute or the National Democratic Institute for International Affairs) could carry out such training, which would equip reform leaders to reconcile their differences peacefully and democratically.
“Fourth, the United States should help reformers obtain and use information technology, perhaps by offering incentives for US companies to invest in the region’s communications infrastructure and information technology. US information technology companies could also help ensure that the Web sites of reformers can remain in operation and could invest in technologies such as anonymizers that could offer some shelter from government scrutiny. This could also be accomplished by employing technological safegaurds to prevent regimes from sabotaging the Web sites of reformers. “15
As their Kefaya monograph states, it was prepared in 2008 by the “RAND National Security Research Division’s Alternative Strategy Initiative, sponsored by the Rapid Reaction Technology Office in the Office of the Undersecretary of Defense for Acquisition, Technology, and Logistics.
The Alternative Strategy Initiative, just to underscore the point, includes “research on creative use of the media, radicalization of youth, civic involvement to stem sectarian violence, the provision of social services to mobilize aggrieved sectors of indigenous populations, and the topic of this volume, alternative movements.“16
In May 2009 just before Obama’s Cairo trip to meet Mubarak, US Secretary of State Hillary Clinton hosted a number of the young Egyptian activists in Washington under the auspices of Freedom House, another “human rights” Washington-based NGO with a long history of involvement in USsponsored regime change from Serbia to Georgia to Ukraine and other Color Revolutions. Clinton and Acting Assistant Secretary of State for Near Eastern Affairs Jeffrey Feltman met the sixteen activists at the end of a two-month “fellowship” organized by Freedom House’s New Generation program.17
Freedom House and Washington’s government-funded regime change NGO, National Endowment for Democracy (NED) are at the heart of the uprisings now sweeping across the Islamic world. They fit the geographic context of what George W. Bush proclaimed after 2001 as his Greater Middle East Project to bring “democracy” and “liberal free market” economic reform to the Islamic countries from Afghanistan to Morocco. When Washington talks about introducing “liberal free market reform” people should watch out. It is little more than code for bringing those economies under the yoke of the dollar system and all that implies.
Washington’s NED in a larger agenda
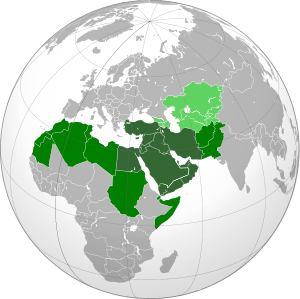
If we make a list of the countries in the region which are undergoing mass-based protest movements since the Tunisian and Egyptian events and overlay them onto a map, we find an almost perfect convergence between the protest countries today and the original map of the Washington Greater Middle East Project that was first unveiled during the George W. Bush Presidency after 2001.
Washington’s NED has been quietly engaged in preparing a wave of regime destabilizations across North Africa and the Middle East since the 2001-2003 US military invasions of Afghanistan and Iraq. The list of where the NED is active is revealing. Its website lists Tunisia, Egypt, Jordan, Kuwait, Libya, Syria, Yemen and Sudan as well, interestingly, as Israel. Coincidentally these countries are almost all today subject to “spontaneous” popular regime-change uprisings.
The International Republican Institute and the National Democratic Institute for International Affairs mentioned by the RAND document study of Kefaya are subsidiary organizations of the Washington-based and US Congress-financed National Endowment for Democracy.
The NED is the coordinating Washington agency for regime destabilization and change. It is active from Tibet to Ukraine, from Venezuela to Tunisia, from Kuwait to Morocco in reshaping the world after the collapse of the Soviet Union into what George H.W. Bush in a 1991 speech to Congress proclaimed triumphantly as the dawn of a New World Order.18
As the architect and first head of the NED, Allen Weinstein told the Washington Post in 1991 that, “a lot of what we do today was done covertly 25 years ago by the CIA“19
The NED Board of Directors includes or has included former Defense Secretary and CIA Deputy head, Frank Carlucci of the Carlyle Group; retired General Wesley Clark of NATO; neo-conservative warhawk Zalmay Khalilzad who was architect of George W. Bush’s Afghan invasion and later ambassador to Afghanistan as well as to occupied Iraq. Another NED board member, Vin Weber, co-chaired a major independent task force on US Policy toward Reform in the Arab World with former US Secretary of State Madeleine Albright, and was a founding member of the ultra-hawkish Project for a New American Century think-tank with Dick Cheney and Don Rumsfeld, which advocated forced regime change in Iraq as early as 1998.20
The NED is supposedly a private, non-government, non-profit foundation, but it receives a yearly appropriation for its international work from the US Congress. The National Endowment for Democracy is dependent on the US taxpayer for funding, but because NED is not a government agency, it is not subject to normal Congressional oversight.
NED money is channelled into target countries through four “core foundations”—the National Democratic Institute for International Affairs, linked to the Democratic Party; the International Republican Institute tied to the Republican Party; the American Center for International Labor Solidarity linked to the AFL-CIO US labor federation as well as the US State Department; and the Center for International Private Enterprise linked to the free-market US Chamber of Commerce.
The late political analyst Barbara Conry noted that,
“NED has taken advantage of its alleged private status to influence foreign elections, an activity that is beyond the scope of AID or USIA and would otherwise be possible only through a CIA covert operation. Such activities, it may also be worth noting, would be illegal for foreign groups operating in the United States.”21
Significantly the NED details its various projects today in Islamic countries, including in addition to Egypt, in Tunisia, Yemen, Jordan, Algeria, Morocco, Kuwait, Lebanon, Libya, Syria, Iran and Afghanistan. In short, most every country which is presently feeling the earthquake effects of the reform protests sweeping across the Middle East and North Africa is a target of NED.22
In 2005 US President George W. Bush made a speech to the NED. In a long, rambling discourse which equated “Islamic radicalism” with the evils of communism as the new enemy, and using a deliberately softer term “broader Middle East” for the term Greater Middle East that had aroused much distruct in the Islamic world, Bush stated,
“The fifth element of our strategy in the war on terror is to deny the militants future recruits by replacing hatred and resentment with democracy and hope across the broader Middle East. This is a difficult and long-term project, yet there’s no alternative to it. Our future and the future of that region are linked. If the broader Middle East is left to grow in bitterness, if countries remain in misery, while radicals stir the resentments of millions, then that part of the world will be a source of endless conflict and mounting danger, and for our generation and the next. If the peoples of that region are permitted to choose their own destiny, and advance by their own energy and by their participation as free men and women, then the extremists will be marginalized, and the flow of violent radicalism to the rest of the world will slow, and eventually end… We’re encouraging our friends in the Middle East, including Egypt and Saudi Arabia, to take the path of reform, to strengthen their own societies in the fight against terror by respecting the rights and choices of their own people. We’re standing with dissidents and exiles against oppressive regimes, because we know that the dissidents of today will be the democratic leaders of tomorrow…”23
The US Project for a ‘Greater Middle East’
The spreading regime change operations by Washington from Tunisia to Sudan, from Yemen to Egypt to Syria are best viewed in the context of a long-standing Pentagon and State Department strategy for the entire Islamic world from Kabul in Afghanistan to Rabat in Morocco.
The rough outlines of the Washington strategy, based in part on their successful regime change operations in the former Warsaw Pact communist bloc of Eastern Europe, were drawn up by former Pentagon consultant and neo-conservative, Richard Perle and later Bush official Douglas Feith in a white paper they drew up for the then-new Israeli Likud regime of Benjamin Netanyahu in 1996.
That policy recommendation was titled A Clean Break: A New Strategy for Securing the Realm. It was the first Washington think-tank paper to openly call for removing Saddam Hussein in Iraq, for an aggressive military stance toward the Palestinians, striking Syria and Syrian targets in Lebanon.24
Reportedly, the Netanyahu government at that time buried the Perle-Feith report, as being far too risky. By the time of the events of September 11, 2001 and the return to Washington of the arch war hawk neoconservatives around Perle and others, the Bush Administration put highest priority on an expanded version of the Perle-Feith paper, calling it their Greater Middle East Project. Feith was named Bush’s Under Secretary of Defense.
Behind the facade of proclaiming democratic reforms of autocratic regimes in the entire region, the Greater Middle East was and is a blueprint to extend US military control and to break open the statist economies in the entire span of states from Morocco to the borders of China and Russia.
In May 2005, before the rubble from the US bombing of Baghdad had cleared, George W. Bush, a President not remembered as a great friend of democracy, proclaimed a policy of “spreading democracy” to the entire region and explicitly noted that that meant “the establishment of a USMiddle East free trade area within a decade.” 25
Prior to the June 2004 G8 Summit on Sea Island, Georgia, Washington issued a working paper, “G8-Greater Middle East Partnership.” Under the section titled Economic Opportunities was Washington’s dramatic call for “an economic transformation similar in magnitude to that undertaken by the formerly communist countries of Central and Eastern Europe.”
The US paper said that the key to this would be the strengthening of the private sector as the way to prosperity and democracy. It misleadingly claimed it would be done via the miracle of microfinance where as the paper put it, “a mere $100 million a year for five years will lift 1.2 million entrepreneurs (750,000 of them women) out of poverty, through $400 loans to each.” 26
The US plan envisioned takeover of regional banking and financial affairs by new institutions ostensibly international but, like World Bank and IMF, de facto controlled by Washington, including WTO. The goal of Washington’s long-term project is to completely control the oil, to completely control the oil revenue flows, to completely control the entire economies of the region, from Morocco to the borders of China and all in between. It is a project as bold as it is desperate.
Once the G8 US paper was leaked in 2004 in the Arabic Al-Hayat, opposition to it spread widely across the region, with a major protest to the US definition of the Greater Middle East. As an article in the French Le Monde Diplomatique in April 2004 noted, “besides the Arab countries, it covers Afghanistan, Iran, Pakistan, Turkey and Israel, whose only common denominator is that they lie in the zone where hostility to the US is strongest, in which Islamic fundamentalism in its anti-Western form is most rife.“27 It should be noted that the NED is also active inside Israel with a number of programs.
Notably, in 2004 it was vehement opposition from two Middle East leaders—Hosni Mubarak of Egypt and the King of Saudi Arabia—that forced the ideological zealots of the Bush Administration to temporarily put the Project for the Greater Middle East on a back burner.
Will it work?
At this writing it is unclear what the ultimate upshot of the latest US-led destabilizations across the Islamic world will bring. It is not clear what will result for Washington and the advocates of a USdominated New World Order. Their agenda is clearly one of creating a Greater Middle East under firm US grip as a major control of the capital flows and energy flows of a future China, Russia and a European Union that might one day entertain thoughts of drifting away from that American order.
It has huge potential implications for the future of Israel as well. As one US commentator put it, “The Israeli calculation today is that if ‘Mubarak goes’ (which is usually stated as ‘If America lets Mubarak go’), Egypt goes. If Tunisia goes (same elaboration), Morocco and Algeria go. Turkey has already gone (for which the Israelis have only themselves to blame). Syria is gone (in part because Israel wanted to cut it off from Sea of Galilee water access). Gaza has gone to Hamas, and the Palestine Authority might soon be gone too (to Hamas?). That leaves Israel amid the ruins of a policy of military domination of the region.” 28
The Washington strategy of “creative destruction” is clearly causing sleepless nights not only in the Islamic world but also reportedly in Tel Aviv, and ultimately by now also in Beijing and Moscow and across Central Asia.
1 DEBKA, Mubarak believes a US-backed Egyptian military faction plotted his ouster, February 4, 2011, accessed in www.debka.com/weekly/480/. DEBKA is open about its good ties to Israeli intelligence and security agencies. While its writings must be read with that in mind, certain reports they publish often contain interesting leads for further investigation.
2 Ibid.
3 The Center for Grassroots Oversight, 1954-1970: CIA and the Muslim Brotherhood ally to oppose Egyptian President Nasser, www.historycommons.org/context.jsp?item=western_support_for_islamic_militancy_202700&scale=0. According to the late Miles Copeland, a CIA official stationed in Egypt during the Nasser era, the CIA allied with the Muslim Brotherhood which was opposed to Nasser’s secular regime as well as his nationalist opposition to brotherhood pan-Islamic ideology.
4 Jijo Jacob, What is Egypt’s April 6 Movement?, February 1, 2011, accessed in http://www.ibtimes.com/articles/107387/20110201/what-is-egypt-s-april-6-movement.htm
5 Ibid.
6 Janine Zacharia, Opposition groups rally around Mohamed ElBaradei, Washington Post, January 31, 2011, accessed in .
7 National Endowment for Democracy, Middle East and North Africa Program Highlights 2009, accessed in http://www.ned.org/where-we-work/middle-east-and-northern-africa/middle-east-and-north-africahighlights.
8 Amitabh Pal, Gene Sharp: The Progressive Interview, The Progressive, March 1, 2007.
9 Emmanuel Sivan, Why Radical Muslims Aren’t Taking over Governments, Middle East Quarterly, December 1997, pp. 3-9
10 Carnegie Endowment, The Egyptian Movement for Change (Kifaya), accessed in http://egyptelections.carnegieendowment.org/2010/09/22/the-egyptian-movement-for-change-kifaya
11 Nadia Oweidat, et al, The Kefaya Movement: A Case Study of a Grassroots Reform Initiative, Prepared for the Office of the Secretary of Defense, Santa Monica, Ca., RAND_778.pdf, 2008, p. iv.
12 Ibid.
13 For a more detailed discussion of the RAND “swarming” techniques see F. William Engdahl, Full Spectrum Dominance: Totalitarian Democracy in the New World Order, edition.engdahl, 2009, pp. 34-41.
14 Nadia Oweidat et al, op. cit., p. 48.
15 Ibid., p. 50.
16 Ibid., p. iii.
17 Michel Chossudovsky, The Protest Movement in Egypt: “Dictators” do not Dictate, They Obey Orders, January 29, 2011, accessed in https://www.globalresearch.ca/the-protest-movement-in-egypt-dictators-do-not-dictate-they-obey-orders/22993
18 George Herbert Walker Bush, State of the Union Address to Congress, 29 January 1991. In the speech Bush at one point declared in a triumphant air of celebration of the collapse of the Sovoiet Union, “What is at stake is more than one small country, it is a big idea—a new world order…”
19 Allen Weinstein, quoted in David Ignatius, Openness is the Secret to Democracy, Washington Post National Weekly Edition, 30 September 1991, pp. 24-25.
20 National Endowment for Democracy, Board of Directors, accessed in
21 Barbara Conry, Loose Cannon: The National Endowment for Democracy, Cato Foreign Policy Briefing No. 27, November 8, 1993, accessed in .
22 National Endowment for Democracy, 2009 Annual Report, Middle East and North Africa, accessed in http://www.ned.org/publications/annual-reports/2009-annual-report.
23 George W. Bush, Speech at the National Endowment for Democracy, Washington, DC, October 6, 2005,accessed in http://www.presidentialrhetoric.com/speeches/10.06.05.html.
24 Richard Perle, Douglas Feith et al, A Clean Break: A New Strategy for Securing the Realm, 1996, Washington and Tel Aviv, The Institute for Advanced Strategic and Political Studies, accessed in www.iasps.org/strat1.htm
25 George W. Bush, Remarks by the President in Commencement Address at the University of South Carolina, White House, 9 May 2003.
26 Gilbert Achcar, Fantasy of a Region that Doesn’t Exist: Greater Middle East, the US plan, Le Monde Diplomatique, April 4, 2004, accessed in https://mondediplo.com/2004/04/04world
27 Ibid.
28 William Pfaff, American-Israel Policy Tested by Arab Uprisings, accessed in http://www.truthdig.com/report/item/american-israeli_policy_tested_by_arab_uprisings_20110201/
http://www.engdahl.oilgeopolitics.net/print/Creative%20Destruction%20Washington%20Style.pdf