by F. William Engdahl

Global Research, July 11, 2009
https://www.globalresearch.ca/washington-is-playing-a-deeper-game-with-china/14327
After the tragic events of July 5 in Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region in China, it would be useful to look more closely into the actual role of the US Government’s ”independent“ NGO, the National Endowment for Democracy (NED). All indications are that the US Government, once more acting through its “private” Non-Governmental Organization, the NED, is massively intervening into the internal politics of China.
The reasons for Washington’s intervention into Xinjiang affairs seems to have little to do with concerns over alleged human rights abuses by Beijing authorities against Uyghur people. It seems rather to have very much to do with the strategic geopolitical location of Xinjiang on the Eurasian landmass and its strategic importance for China’s future economic and energy cooperation with Russia, Kazakhastan and other Central Asia states of the Shanghai Cooperation Organization.
The major organization internationally calling for protests in front of Chinese embassies around the world is the Washington, D.C.-based World Uyghur Congress (WUC).
The WUC manages to finance a staff, a very fancy website in English, and has a very close relation to the US Congress-funded NED. According to published reports by the NED itself, the World Uyghur Congress receives $215,000.00 annually from the National Endowment for Democracy for “human rights research and advocacy projects.” The president of the WUC is an exile Uyghur who describes herself as a “laundress turned millionaire,” Rebiya Kadeer, who also serves as president of the Washington D.C.-based Uyghur American Association, another Uyghur human rights organization which receives significant funding from the US Government via the National Endowment for Democracy.
The NED was intimately involved in financial support to various organizations behind the Lhasa ”Crimson Revolution“ in March 2008, as well as the Saffron Revolution in Burma/Myanmar and virtually every regime change destabilization in eastern Europe over the past years from Serbia to Georgia to Ukraine to Kyrgystan to Teheran in the aftermath of the recent elections.
Allen Weinstein, who helped draft the legislation establishing NED, was quite candid when he said in a published interview in 1991: “A lot of what we do today was done covertly 25 years ago by the CIA.”
The NED is supposedly a private, non-government, non-profit foundation, but it receives a yearly appropriation for its international work from the US Congress. The NED money is channelled through four “core foundations”. These are the National Democratic Institute for International Affairs, linked to Obama’s Democratic Party; the International Republican Institute tied to the Republican Party; the American Center for International Labor Solidarity linked to the AFL-CIO US labor federation as well as the US State Department; and the Center for International Private Enterprise linked to the US Chamber of Commerce.
The salient question is what has the NED been actively doing that might have encouraged the unrest in Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region, and what is the Obama Administration policy in terms of supporting or denouncing such NED-financed intervention into sovereign politics of states which Washington deems a target for pressure? The answers must be found soon, but one major step to help clarify Washington policy under the new Obama Administration would be for a full disclosure by the NED, the US State Department and NGO’s linked to the US Government, of their involvement, if at all, in encouraging Uyghur separatism or unrest. Is it mere coincidence that the Uyghur riots take place only days following the historic meeting of the Shanghai Cooperation Organization?
Uyghur exile organizations, China and Geopolitics
On May 18 this year, the US-government’s in-house “private” NGO, the NED, according to the official WUC website, hosted a seminal human rights conference entitled East Turkestan: 60 Years under Communist Chinese Rule, along with a curious NGO with the name, the Unrepresented Nations and Peoples Organisation (UNPO).
The Honorary President and founder of the UNPO is one Erkin Alptekin, an exile Uyghur who founded UNPO while working for the US Information Agency’s official propaganda organization, Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty as Director of their Uygur Division and Assistant Director of the Nationalities Services.
Alptekin also founded the World Uyghur Congress at the same time, in 1991, while he was with the US Information Agency. The official mission of the USIA when Alptekin founded the World Uyghur Congress in 1991 was “to understand, inform, and influence foreign publics in promotion of the [USA] national interest…” Alptekin was the first president of WUC, and, according to the official WUC website, is a “close friend of the Dalai Lama.”
Closer examination reveals that UNPO in turn to be an American geopolitical strategist’s dream organization. It was formed, as noted, in 1991 as the Soviet Union was collapsing and most of the land area of Eurasia was in political and economic chaos. Since 2002 its Director General has been Archduke Karl von Habsburg of Austria who lists his (unrecognized by Austria or Hungary) title as “Prince Imperial of Austria and Royal Prince of Hungary.”
Among the UNPO principles is the right to ‘self-determination’ for the 57 diverse population groups who, by some opaque process not made public, have been admitted as official UNPO members with their own distinct flags, with a total population of some 150 million peoples and headquarters in the Hague, Netherlands.
UNPO members range from Kosovo which “joined” when it was fully part of then Yugoslavia in 1991. It includes the “Aboriginals of Australia” who were listed as founding members along with Kosovo. It includes the Buffalo River Dene Nation indians of northern Canada.
The select UNPO members also include Tibet which is listed as a founding member. It also includes other explosive geopolitical areas as the Crimean Tartars, the Greek Minority in Romania, the Chechen Republic of Ichkeria (in Russia), the Democratic Movement of Burma, and the gulf enclave adjacent to Angola and the Democratic Republic of the Congo, and which just happens to hold rights to some of the world’s largest offshore oil fields leased to Condi Rice’s old firm, Chevron Oil. Further geopolitical hotspots which have been granted elite recognition by the UNPO membership include the large section of northern Iran which designates itself as Southern Azerbaijan, as well as something that calls itself Iranian Kurdistan.
In April 2008 according to the website of the UNPO, the US Congress’ NED sponsored a “leadership training” seminar for the World Uyghur Congress (WUC) together with the Unrepresented Nations and Peoples Organization. Over 50 Uyghurs from around the world together with prominent academics, government representatives and members of the civil society gathered in Berlin Germany to discuss “Self-Determination under International Law.” What they discussed privately is not known. Rebiya Kadeer gave the keynote address.
The suspicious timing of the Xinjiang riots
The current outbreak of riots and unrest in Urumqi, the capital of Xinjiang in the northwest part of China, exploded on July 5 local time.
According to the website of the World Uyghur Congress, the “trigger” for the riots was an alleged violent attack on June 26 in China’s southern Guangdong Province at a toy factory where the WUC alleges that Han Chinese workers attacked and beat to death two Uyghur workers for allegedly raping or sexually molesting two Han Chinese women workers in the factory. On July 1, the Munich arm of the WUC issued a worldwide call for protest demonstrations against Chinese embassies and consulates for the alleged Guangdong attack, despite the fact they admitted the details of the incident were unsubstantiated and filled with allegations and dubious reports.
According to a press release they issued, it was that June 26 alleged attack that gave the WUC the grounds to issue their worldwide call to action.
On July 5, a Sunday in Xinjiang but still the USA Independence Day, July 4, in Washington, the WUC in Washington claimed that Han Chinese armed soldiers seized any Uyghur they found on the streets and according to official Chinese news reports, widespread riots and burning of cars along the streets of Urumqi broke out resulting over the following three days in over 140 deaths.
China’s official Xinhua News Agency said that protesters from the Uighur Muslim ethnic minority group began attacking ethnic Han pedestrians, burning vehicles and attacking buses with batons and rocks. “They took to the street…carrying knives, wooden batons, bricks and stones,” they cited an eyewitness as saying. The French AFP news agency quoted Alim Seytoff, general secretary of the Uighur American Association in Washington, that according to his information, police had begun shooting “indiscriminately” at protesting crowds.
Two different versions of the same events: The Chinese government and pictures of the riots indicate it was Uyghur riot and attacks on Han Chinese residents that resulted in deaths and destruction. French official reports put the blame on Chinese police “shooting indiscriminately.” Significantly, the French AFP report relies on the NED-funded Uyghur American Association of Rebiya Kadeer for its information. The reader should judge if the AFP account might be motivated by a US geopolitical agenda, a deeper game from the Obama Administration towards China’s economic future.
Is it merely coincidence that the riots in Xinjiang by Uyghur organizations broke out only days after the meeting took place in Yakaterinburg, Russia of the member nations of the Shanghai Cooperation Organization, as well as Iran as official observer guest, represented by President Ahmadinejad?
Over the past few years, in the face of what is seen as an increasingly hostile and incalculable United States foreign policy, the major nations of Eurasia—China, Russia, Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan have increasingly sought ways of direct and more effective cooperation in economic as well as security areas. In addition, formal Observer status within SCO has been given to Iran, Pakistan, India and Mongolia. The SCO defense ministers are in regular and growing consultation on mutual defense needs, as NATO and the US military command continue provocatively to expand across the region wherever it can.
The Strategic Importance of Xinjiang for Eurasian Energy Infrastructure
There is another reason for the nations of the SCO, a vital national security element, to having peace and stability in China’s Xinjiang region. Some of China’s most important oil and gas pipeline routes pass directly through Xinjiang province. Energy relations between Kazkhstan and China are of enormous strategic importance for both countries, and allow China to become less dependent on oil supply sources that can be cut off by possible US interdiction should relations deteriorate to such a point.
Kazak President Nursultan Nazarbayev paid a State visit in April 2009 to Beijing. The talks concerned deepening economic cooperation, above all in the energy area, where Kazkhastan holds huge reserves of oil and likely as well of natural gas. After the talks in Beijing, Chinese media carried articles with such titles as “”Kazakhstani oil to fill in the Great Chinese pipe.”
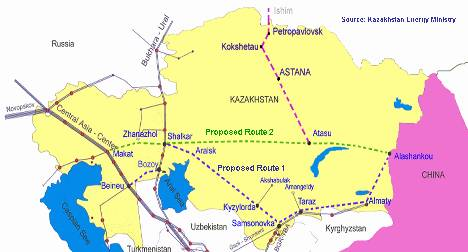
The Atasu-Alashankou pipeline to be completed in 2009 will provide transportation of transit gas to China via Xinjiang. As well Chinese energy companies are involved in construction of a Zhanazholskiy gas processing plant, Pavlodar electrolyze plant and Moynakskaya hydro electric station in Kazakhstan.
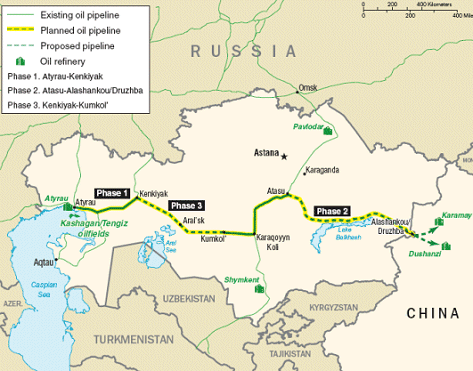
According to the US Government’s Energy Information Administration, Kazakhstan’s Kashagan field is the largest oil field outside the Middle East and the fifth largest in the world in terms of reserves, located off the northern shore of the Caspian Sea, near the city of Atyrau. China has built a 613-mile-long pipeline from Atasu, in northwestern Kazakhstan, to Alashankou at the border of China’s Xinjiang region which is exporting Caspian oil to China. PetroChina’s ChinaOil is the exclusive buyer of the crude oil on the Chinese side. The pipeline is a joint venture of CNPC and Kaztransoil of Kazkhstan. Some 85,000 bbl/d of Kazakh crude oil flowed through the pipeline during 2007. China’s CNPC is also involved in other major energy projects with Kazkhstan. They all traverse China’s Xinjiang region.
In 2007 CNPC signed an agreement to invest more than $2 billion to construct a natural gas pipeline from Turkmenistan through Uzbekistan and Kazakhstan to China. That pipeline would start at Gedaim on the border of Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan and extend 1,100 miles through Uzbekistan and Kazakhstan to Khorgos in China’s Xinjiang region. Turkmenistan and China have signed a 30-year supply agreement for the gas that would fill the pipeline. CNPC has set up two entities to oversee the Turkmen upstream project and the development of a second pipeline that will cross China from the Xinjiang region to southeast China at a cost of some $7 billion.
As well, Russia and China are discussing major natural gas pipelines from eastern Siberia through Xinjiang into China. Eastern Siberia contains around 135 Trillion cubic feet of proven plus probable natural gas reserves. The Kovykta natural gas field could give China with natural gas in the next decade via a proposed pipeline.
During the current global economic crisis, Kazakhstan received a major credit from China of $10 billion, half of which is for oil and gas sector. The oil pipeline Atasu-Alashankou and the gas pipeline China-Central Asia, are an instrument of strategic ‘linkage’ of central Asian countries to the economy China. That Eurasian cohesion from Russia to China across Central Asian countries is the geopolitical cohesion Washington most fears. While they would never say so, growing instability in Xinjiang would be an ideal way for Washington to weaken that growing cohesion of the Shanghai Cooperation Organization nations.
William Engdahl is the author of Full Spectrum Dominance: Totalitarian Democracy in the New World Order.







