Turkey, Iran: Ankara’s Priorities ShiftAugust 15, 2008 | 2146 GMT
BULENT KILIC/AFP/Getty Images
Iranian President Mahmoud Ahmadinejad (L) and Turkish President Abdullah Gul in Istanbul
Summary
Iranian President Mahmoud Ahmadinejad’s two-day trip to Ankara ended Aug. 15. While the Iranian government and state media have touted his trip as proof that Iran and Turkey are close allies, the Turkish government is far more concerned with containing the current situation in the Caucasus, which could have major implications for Turkey’s ally Azerbaijan.
Analysis
Iranian President Mahmoud Ahmadinejad wrapped up a two-day trip to Ankara on Aug. 15. The Iranian government and state media have been hyping Ahmadinejad’s visit to Turkey for days in an attempt to showcase to the world the Iranian belief that Iran and Turkey, as the two principle non-Arab regional powerhouses, are close and natural allies.
But while Iran is eager to forge closer ties with Turkey, the Turks do not have much time for Ahmadinejad right now. Ankara has bigger things on its mind, namely the Russians.
Turkey is heir to the Ottoman Empire, which once extended deep into the southern Caucasus region where Russia just wrapped up an aggressive military campaign against Georgia. Turkey’s geopolitical interests in the Caucasus have primarily been defensive in nature, focused on keeping the Russians and Persians at bay. Now that Russia is resurging in the Caucasus, the Turks have no choice but to get involved.
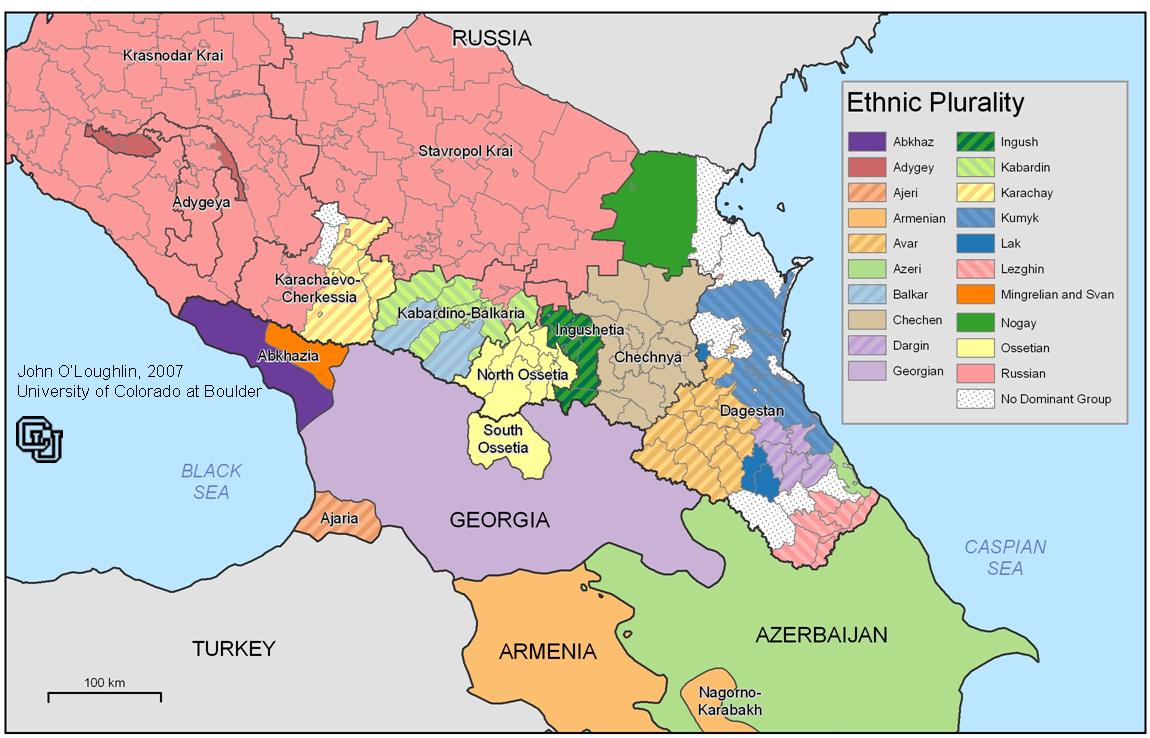
The Turks primarily rely on their deep ethnic, historical and linguistic ties to Azerbaijan to extend their influence into the Caucasus. Azerbaijan was alarmed, to say the least, when it saw Russian tanks crossing into Georgia. As far as Azerbaijan was concerned, Baku could have been the next target in Russia’s military campaign.
However, Armenia — Azerbaijan’s primary rival — remembers well the 1915 Armenian genocide by the Turks, and looks to Iran and especially Orthodox Christian Russia for its protection. Now that Russia has shown it is willing to act on behalf of allies like South Ossetia and Abkhazia in the Caucasus, the Armenians, while militarily outmatched by the Azerbaijanis, are now feeling bolder and could see this as their chance to preempt Azerbaijan in yet another battle for the disputed Nagorno-Karabakh region— especially if it thinks it can look to Russia to militarily intervene on its behalf.
The Turks and their ethnic kin in Azerbaijan are extremely wary of Russia’s intentions for the southern Caucasus beyond Georgia. Sources told Stratfor that Azerbaijan has learned that the Russian military jets that bombed Gori and Poti were based out of Armenia. This development not only signaled a significant expansion of Russia’s military presence in the southern Caucasus, but it also implied that Armenia had actually signed off on the Russian foray into Georgia, knowing that Russian dominance over Georgia would guarantee Armenian security and impose a geographic split between Turkey and Azerbaijan. If the Armenians became overly confident and made a move against Azerbaijan for Nagorno-Karabakh, expecting Russian support, the resulting war would have a high potential of drawing the Turks into a confrontation with the Russians — something that both NATO member Turkey and Ru ssia have every interest in avoiding.
The Turks also have a precarious economic relationship with Russia. The two countries have expanded their trade with each other significantly in recent years. In the first half of 2008, trade between Russia and Turkey amounted to $19.9 billion, making Russia Turkey’s biggest trading partner. Much of this trade is concentrated in the energy sphere. The Turks currently import approximately 64 percent of the natural gas they consume from the Russians. Though Turkey’s geographic position enables it to pursue energy links in the Middle East and the Caucasus that can bypass Russian territory, the Russians have made it abundantly clear over the past few days that the region’s energy security will still depend on Moscow’s good graces.
Turkey’s economic standing also largely depends on its ability to act as a major energy transit hub for the West through pipelines such as the Baku-Tbilisi-Ceyhan (BTC) pipeline, which was recently forced offline due to a purported Kurdish militant attack and the war in Georgia. Turkey simply cannot afford to see the Russians continue their surge into the Caucasus and threaten its energy supply.
For these reasons, Turkey is on a mission to keep this tinderbox in the Caucasus contained. Turkish Prime Minister Recep Tayyip Erdogan spent the last couple of days meeting with top Russian leaders in Moscow and then with the Georgian president in Tbilisi. During his meetings with Russian Prime Minister Vladimir Putin, President Dmitri Medvedev and Foreign Minister Sergei Lavrov, Erdogan pushed the idea of creating a Caucasus union that would include both Russia and Georgia. Though this organization would likely be little more than a talk shop, it is a sign of Turkey’s interest in reaching a mutual understanding with Russia that would allow both sides to maintain a comfortable level of influence in the region without coming to blows..
The Iranians, meanwhile, are sitting in the backseat. Though Iran has a foothold in the Caucasus through its support for Armenia, the Iranians lack the level of political, military and economic gravitas that Turkey and Russia currently hold in this region. Indeed, Erdogan did not even include Iran in his list of proposed members for the Caucasus union, even though Iran is one of the three major powers bordering the region. The Turks also struck a blow to Iran by holding back from giving Ahmadinejad the satisfaction of sealing a key energy agreement for Iran to provide Turkey with natural gas, preferring instead to preserve its close relationship with the United States and Israel. Turkey simply is not compelled to give Iran the attention that it is seeking at the moment.
The one thing that Turkey can look to Iran for, however, is keeping the Armenia-Azerbaijan conflict under control. Iran’s support for Armenia has naturally put Tehran on a collision course with Ankara when dealing with the Caucasus in the past. But when faced with a common threat of a resurgent Russia, both Turkey and Iran can agree to disagree on their conflicting interests in this region and use their leverage to keep Armenia or Azerbaijan from firing off a shot and pulling the surrounding powers into a broader conflict. In light of the recent BTC explosion claimed by the Kurdistan Workers’ Party (PKK), Turkey can also look to Iran to play its part in cracking down on PKK rebels in the region, many of whom have spent the past year fleeing a Turkish crackdown in northern Iraq by traversing through Iran to reach the southern Caucasus.
While Iran and Turkey can cooperate in fending off the Russians, it will primarily be up to Turkey to fight the battle in the Caucasus. Russia has thus far responded positively to Turkey’s diplomatic engagements, but in a region with so many conflicting interests, the situation could change in a heartbeat.
|
|
Category: Asia and Pacific
-

STRATFOR : Turkey, Iran: Ankara’s Priorities Shift
-

Azerbaijan: The Stark New Energy Landscape
August 15, 2008 | 1817 GMT
Yoray Liberman/Getty Images
Workers at the Baku-Tbilisi-Ceyhan pipeline terminal in Turkey
Summary
Russia’s military defeat of Georgia puts Azerbaijan in a difficult position. With all of its existing energy export routes now back under Russian control, Baku faces a stark set of choices that may force it to reach an accommodation with Moscow.
Analysis
Related Links
- Turkey: An Oil Pipeline Fire and the Russian Alternative
- Russia: Courting Azerbaijan for Natural Gas
- Global Market Brief: BP Takes a Hit in the Georgia Conflict
Related Special Topic Pages
- Central Asian Energy: Circumventing Russia
- The Russian Resurgence
- Russian Energy and Foreign Policy
- Crisis in South Ossetia
Azerbaijan is losing some $50 million to $70 million per day due to the closure of the Baku-Tbilisi-Ceyhan (BTC) oil pipeline, the Caspian Energy Alliance said Aug. 14, adding that Baku’s total losses from the closure amounted to some $500 million. The 1 million barrel per day (bpd) BTC line, which passes from Azerbaijan to Turkey via Georgia, was shut down Aug. 6 following an attack on the Turkish part of the line, claimed by a Kurdish separatist group. If not for that attack, however, it might well have been shut down anyway amid the military conflict in Georgia that began two days later.
Azerbaijan exports oil and natural gas to Western energy markets via three pipelines — all of which pass through Georgia, and all of which experienced cutoffs in the past several days. Two
of them — the BTC and the 150,000 bpd Baku-Supsa — carry oil. The Baku-Tbilisi-Erzurum line carries natural gas at 9 billion cubic meters per year. The pipelines were built to provide a transport route for Caspian Sea energy to reach Western markets without having to pass through Russia, which controls the majority of pipeline infrastructure into Europe. Now that Russia has established a firm military presence in Georgia, however, it is highly likely that all three lines will continue to operate, or not, at the pleasure of the Kremlin.This puts Azerbaijan in a predicament. With its export routes to the West blocked by the Russian presence in Georgia, Baku is carefully considering its options. Though other potential pipeline routes exist, they are plagued with problems that could prove insurmountable. Azerbaijan may have no real option but to try to reach some sort of accommodation with Moscow.
Initially, Baku was excited by the conflict in Georgia’s South Ossetia region because it provided a possible blueprint for dealing with Azerbaijan’s own restive separatist enclave of Nagorno-Karabakh — and for potentially imposing a new military reality on Baku’s regional rival, Armenia.. If successful, such a campaign could have allowed Baku to use Armenian territory for a new energy export route. Sources tell Stratfor that, following the Georgian military’s Aug. 8 invasion of South Ossetia, Azerbaijan’s leadership convened an emergency meeting at which they reportedly gave serious consideration to invading Nagorno-Karabakh, contingent on the eventual success of the Georgian operation.
However, the Georgian offensive not only failed, it resulted in the Russian invasion of Georgia proper — which has effectively suspended Tbilisi’s ability to control its own territory. Russia also used air bases in Armenia to assist in the Georgian intervention, which marked a significant change in the dynamic between Baku and Yerevan. Russia keeps military assets in both Azerbaijan and Armenia, and sells weapons to both — indeed, part of Moscow’s strategy in the Caucasus is to ensure that the two rivals remain distracted by their tense relations — but from Baku’s perspective, the Russian decision to activate its assets in Armenia means Moscow is choosing sides. However possible it might have been for Azerbaijan to invade its neighbor, it has suddenly become inconceivable.
For Baku, this is the worst-case scenario. Its energy lifelines, intended to circumvent Russian territory, are now under the overt control of the Kremlin, while its alternative of forcing a new path through Armenia is completely taken out.
Baku also suddenly found itself trying to block the flood of Azeri volunteers heading to Georgia to fight the invading Russians. Azerbaijan’s government did not want to provoke Russia, especially with Russian tanks only a couple of hundred miles from Baku itself. For that matter, with a presidential election set for Oct. 15, Azeri President Ilham Aliyev does not want a security crisis on his hands. Even though Azerbaijan has been using its energy revenues to build up its military in recent years, it is nowhere near ready to defend itself from a Russian invasion. Its security situation is in many ways even more dire than that of Georgia (or even Ukraine).
Turkey, Baku’s strongest ally in the region, theoretically would not stand by if Russia invaded Azerbaijan — but then, Ankara has been silent on the Russian intervention in Georgia. To the Azeris, this is a sign that they cannot depend on the Turks to commit themselves to a fight with Moscow if push should come to shove. Also, now that Georgia is under effective Russian military control, the only route for Turkish aid to Azerbaijan is cut off — neither Iran nor Armenia would provide passage.
With the Russians in control of Georgia and with domination of Armenia out of the picture, Azerbaijan’s only other feasible export route would be southward through Iran, hooking into existing Turkish pipeline infrastructure or sending exports out via the Persian Gulf. The problem with this option is one of timing: Any move into Iran would have to wait for an accommodation between Tehran and the United States over Iraq, which appears to be getting ever nearer but could still be derailed. At $50 million in losses per day, however, Azerbaijan does not have the time to wait for these pieces to fall into place and then build a new pipeline into Iran. A Russian move to cut off all three pipelines going through Georgia would make the cost unbearable. Baku counts on i ts energy export revenues in order to maintain military parity with Armenia, so a sharp drop in funding could quickly become a national security issue.
That leaves one other option, which from Baku’s perspective is the least desirable but the most realistic: seeking accommodation with Russia.
Russia now effectively controls the entire already-built energy transport infrastructure between Baku and Western markets. Russia could accommodate transport of Azeri energy through Georgia for the right price. That price would be both financial and political: Azerbaijan would need to align with Moscow on matters of import in order to keep the pipelines open. Baku also could ship its natural gas through Russia proper via pipelines such as Baku-Rostov-on-Don, which used to provide Azerbaijan with natural gas supplies before it became a net exporter. There also is the Baku-Novorossiysk oil pipeline, which has a capacity of nearly 200,000 bpd, although very little Azeri crude normally goes through it.
Azerbaijan has tried to avoid shipping its energy exports through Russian pipelines while other feasible options were open. But Baku may have to reconsider now that Russia holds all the cards.
Terms of Use | Privacy Policy | Contact Us
© Copyright 2008 Strategic Forecasting Inc. All rights reserved. -
Izmir Azerbaijanis begin signature campaign for not opening the Turkish-Armenian border
Izmir-based Azerbaijan Culture Center began signature campaign demanding not to open the Turkish-Armenian border until the withdrawal of Armenian occupier forces from the Azerbaijani lands, APA reports with reference to CHA agency. (more…)
-

Head of American Jewish committee: “Events in Georgia are a historical moment for Azerbaijan”
Events in Georgia are a historical moment for the whole world, especially for Azerbaijan, said chief executive of the American Jewish Community David Harris by results of his visit to Azerbaijan.
He said Azerbaijan has now a chance to show the US how it can help its friends in critical moments. (more…)
-

Head of American Jewish Committee: “We will focus on the 907th amendment on Azerbaijan”
Few Americans know about Azerbaijan’s role in the war in Afghanistan, Iraq and in combat with international terror, said chief executive of the American Jewish Committee David Harris.
He said that people in America do not know that Azerbaijan is an island of tolerance, maintaining good cooperation with Israel. (more…)
-

separate and unequal
From: Arch Getty <getty@ucla.edu>
Subject: separate and unequal
Date: Fri, 15 Aug 2008Things look very different from here in Moscow,
almost as if one is observing things from another planet.The other night I watched a story on Russia
Today, a semi-official Russian news channel. It
showed CNN footage purporting to come from the
apparent Russian “capture” of the Georgian town
of Gori. Actually, the film was (unattributed)
Russia Today footage of damage from the Georgian
attack days ago on Tskhinvali, the So. Ossetian capital.But even aside from the difficulty of getting
anything resembling accurate news here, the
Russian point of view is, predictably, vastly
different from the knee-jerk Russophobia in the
U.S. press. And to many of us here, the Russian
point of view is at least as compelling as the
mainstream U.S. attitudes we hear about.Russians have always been sensitive to western
views of them and are particularly alert for
attitudes that smack of inequality and
hypocrisy. The vast majority of people here are
amazed, sad, and confused at the way the western
media has transformed the Georgian side, which
started the war, into the victims. When Prime
Minister Putin decried the west’s cynical
“turning black into white” he spoke for large numbers of Russians.People here were amazed and insulted when
President Bush bragged about his “stern” warnings
to Putin. Like Putin, they cannot imagine a
reason to pay any attention to such a person,
whose paternalistic but helpless schoolmarm
lectures are considered here to be “not serious.”Russians wonder how, before Russian intervention,
something more than a thousand deaths including
the destruction of villages and shooting of
civilians by the Georgians escape western notice.They wonder why Georgian attempts to suppress the
Ossetian alphabet were not cultural genocide and
Russian defense against Georgian attack is.They wonder how prying Kossovo away from Serbia
was popular self-determination but So. Ossetian
independence from Georgia is not.They wonder how President Bush, who for the sake
of regime change invaded Iraq far from his
shores, nevertheless managed to denounce Russian
use of force and complain that the days of regime change had passed.They wonder why, in 1942 when attacked by Japan,
the U.S. did not follow its own advice about a
“measured response” and stop her counterattack on
Japan at Pearl Harbor. “Were the Japanese the
victims then, just like the Georgians?”They wonder why, as one puzzled but sincere
friend put it, “you Americans hate us so much when we do what you do.”But mostly they wonder why US leaders cannot come
up with a more sophisticated world view for the
21st century than surrounding Russia (which after
all has nuclear weapons and much of the world’s
oil) with verbal abuse, hostile alliances and
provocations. They don’t understand why US
leaders cannot see beyond or outgrow the cold
war. Another asked, “So Cheney and Rice, they
aren’t your most advanced global thinkers, right?”J. Arch Getty
Moscow
[Professor of History, UCLA]Johnson’s Russia List
2008-#150
15 August 2008
